Data Transformer
API Documentation

The DataFrameTransformer class is the core model for transforming dataframes in Laktory. It serializes chained
DataFrame operations and is generally used between a data source and a data sink.
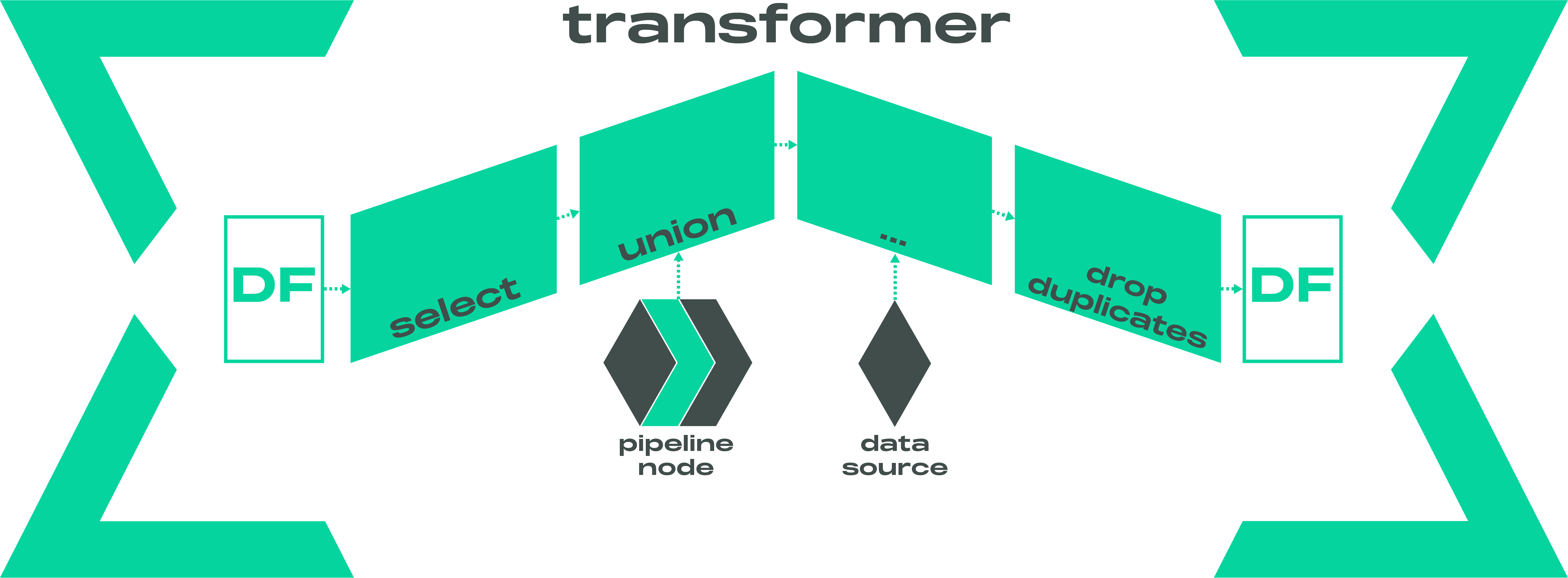
A Transformer is composed of a series of nodes, each representing a transformation applied to a dataframe as an expression or as a method. The output of one node is passed as input to the next, enabling complex and modular transformations.
By default, operations are declared using Narwhals DataFrames API, but it can also be configured to use the selected DataFrame backend API.
DataFrameExpr¤
API Documentation
The DataFrameExpr class expresses a transformation as SELECT SQL expression, including joins and unions.
DataFrameMethod¤
API Documentation
The DataFrameMethod class expresses a transformation as a method applied to the DataFrame and its required arguments.
It supports receiving data sources, including other pipeline nodes, as argument instead of DataFrames. By default,
Narwhals DataFrame API is used, but native DataFrame backend can also be selected. You can also extend this
functionality by creating a custom namespace.
For example, if you have a dataframe with a column x and want to:
- rename
xtothetausing SQL - compute
cos(theta)using Narwhals API - drop duplicated rows using Spark
here is how you would do it:
nodes:
- expr: SELECT x AS theta FROM {df}
- func_name: with_columns
func_kwargs:
cos: nw.col('theta').cost()
- func_name: drop_duplicates
func_args: theta
dataframe_api: NATIVE
import pandas as pd
import laktory as lk
df0 = spark.createDataFrame(pd.DataFrame({"x": [1, 2, 2, 3]}))
# Build Chain
sc = lk.models.DataFrameTransformer(
nodes=[
{
"expr": "SELECT x AS theta FROM {df}",
},
{
"func_name": "with_columns",
"func_kwargs": {
"cos": "nw.col('theta').cos()"
}
},
{
"func_name": "drop_duplicates",
"func_args": ["theta"],
"dataframe_api": "NATIVE",
},
]
)
# Execute Chain
df = sc.execute(df0)
In this example, {df} refers to the output of the previous node in the Spark Chain. You can also
directly reference other pipeline nodes in your SQL queries by using {nodes.node_name}.
For a more modular, scalable, and testable solution, we recommend using Spark over SQL. You can learn more in the blog posts Spark vs SQL and SparkChain .